Tech
Detailed Information About How IPTV Works?
Many programs are broadcasted on different channels everyday. However, you can watch your favorite programs only when they are broadcasted, unless you record them in advance. It would be so good, if TV watching was more similar to browsing the internet whenever you want. Pick any preferred program and watch them from anywhere and at anytime. Advanced IPTV technology provides this facility. It delivers TV program ‘On Demand’ using internet.
IPTV – Definition
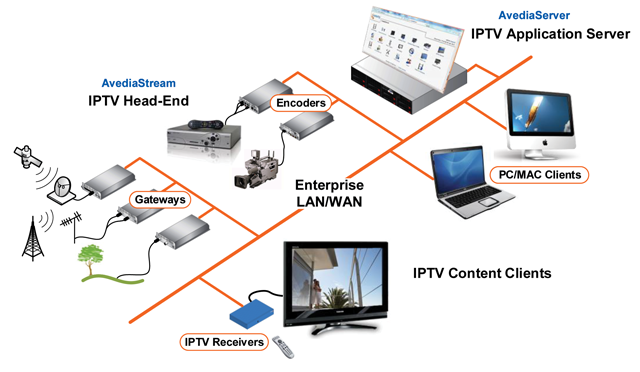
Usual TV programs broadcast signals enter the home through rooftop antenna, fiber optic cable, or satellite dish. In IPTV, the programs are streamed via your broadband internet connection. The program can be watched on a computer or TV through set top box, which decodes incoming signals to display internet programs.
For viewers’ convenience, IPTV companies setup the connection for free. This setting up the IPTV box needs sophisticated storage system and web style interface, so that people can select desired programs.
After the viewer selects a program, there is a need to encode that video file into compatible format for streaming. In addition to this, embed ads and stream it across to millions, simultaneously. The broadcaster has to figure out how to consistently maintain high-quality picture.
Types of IPTV
VOD (Video on Demand) – You pay money for a particular movie or program to be watched there and then.
Time-shifted IPTV – You can watch scheduled broadcasts conveniently.
Live IPTV – Watching live TV program broadcast over the internet as they are watched (similar to standard TV broadcast).
All the three IPTV Forms Work –
- On computer and an normal web browser
- On standard digital TV and set top box
- Over public internet or via managed private network
IPTV – Working Scenario
In a standard TV, radio waves flow in the air and are absorbed by rooftop antenna, which transforms the waves into electrical signal, which is decoded by home TV unit. However, IPTV works a little differently.
How IPTV differs?
Storing programs – The live programs get streamed, as they are produced. Pre-recorded movies and programs need to be stored for streaming on demand.
Preparing programs – TV programs get converted into digital format to get delivered as packages using internet protocol. MPEG4 is latest video compression form, which needs less bandwidth, but provides high quality experience. Later, conversion ads need to be inserted and information encrypted.
Streaming programs – It allows you to access information from other websites and web servers. There is no need to download the files, because you’ll be able to read them as they stream. Servers are powerful and allow clients to download simultaneously, without delay. It is called IP unicasting.
IP multicasting – When you play programs and download simultaneously, extra load is placed on the server, which can cause intolerable delays and buffering. Therefore, a different downloading technology called IP multicasting is used. Each packet is dispatched from the server just once, but is simultaneously distributed to many diverse destinations.
IPTV protocols – Internet practically connects all the global computers because all support to communicate in the same way employing pre-arranged technical protocols. For simultaneous playing and downloading RTSP and RTP protocols are applied. Multi streaming includes the use of IGMP that facilitates one server to televise to group of clients.
Managed networks – Super head end (SHE) stores the program and feeds into video hub offices (VHO), which delivers it to local distribution office linked to set top boxes in different homes.
Everyone can easily switch from ordinary TV viewing to IPTV and start experiencing control, interactivity, and convenience.
-

 Tech11 years ago
Tech11 years agoCreating An e-Commerce Website
-
 Tech11 years ago
Tech11 years agoDesign Template Guidelines For Mobile Apps
-

 Business6 years ago
Business6 years agoWhat Is AdsSupply? A Comprehensive Review
-

 Business10 years ago
Business10 years agoThe Key Types Of Brochure Printing Services
-

 Tech8 years ago
Tech8 years agoWhen To Send Your Bulk Messages?
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years ago5 Link Building Strategies You Can Apply For Local SEO
-

 Law5 years ago
Law5 years agoHow Can A Divorce Lawyer Help You Get Through Divorce?
-

 Home Improvement6 years ago
Home Improvement6 years agoHоw tо Kеер Antѕ Out оf Yоur Kitсhеn